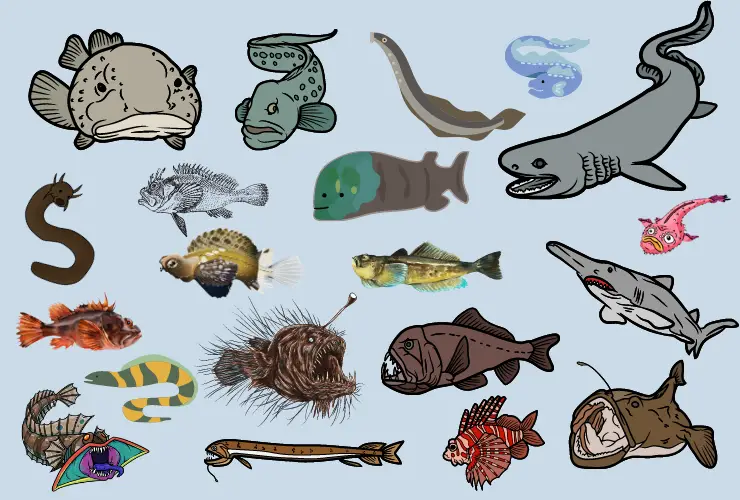
What kind of fascinating sea creatures do you picture when you think of the deep, dark ocean? Something creepy and strange, no doubt. There is a myriad of aquatic creatures with bizarre faces that will surely leave you feeling uneasy. Read on for my list of 20 weird and scary fish in the water.
Before jumping into the detail, here is the chart of 20 weird and scary Halloween fish including the interesting fact and behavior.
| Sl | Fish Name | Interesting Fact |
| 1 | Deep sea anglerfish | The female anglerfish has a glowing lure on her head to attract prey. |
| 2 | Blobfish | The blobfish is actually not as blobby as it appears and looks quite different in its natural habitat. |
| 3 | Frilled shark | The frilled shark has been around since prehistoric times and has a unique tooth structure. |
| 4 | Monkfish | The monkfish has a deliciously unique flavor and texture that is frequently compared with lobster meat. |
| 5 | Goblin shark | The goblin shark has a protruding snout that it uses to detect prey. |
| 6 | Lamprey | The lamprey has cartilaginous skeleton like sharks, but it doesn’t have fins, gill covers and scales. |
| 7 | Dragonfish | The dragonfish can produce its own light and has teeth on its tongue. |
| 8 | Wolf eel | The wolf eel is not a true eel, but a type of fish that can live up to 35 years. |
| 9 | Hagfish | The hagfish can breathe through their skin and nose. |
| 10 | Fangtooth fish | The fangtooth fish has the largest teeth relative to its body size of any fish in the ocean. |
| 11 | Barreleye fish | The barreleye fish has a transparent head and tubular eyes that can rotate to look forward or upward. |
| 12 | Viperfish | The viperfish has a long, needle-like tooth that extends from its lower jaw. |
| 13 | Coffinfish | The coffinfish can inflate itself to make itself look bigger and more intimidating to predators. |
| 14 | Stargazer fish | The stargazer fish has a mouth that faces upward and eyes on the top of its head. |
| 15 | Stonefish | The stonefish is one of the most venomous fish in the world and can be deadly to humans. |
| 16 | Lionfish | The lionfish has long, venomous spines that it uses for protection. |
| 17 | Moray eel | The moray eel has a second set of jaws that can extend from its throat to catch prey. |
| 18 | Scorpionfish | The scorpionfish has venomous spines on its back that it uses for protection. |
| 19 | Sarcastic fringehead | The sarcastic fringehead is a type of fish that can be very territorial and aggressive toward other fish. |
| 20 | Goblinfish | The goblinfish has a large head and a wide mouth, but is relatively small in size. |
20 Weird And Scary Fish
Here is the detail of the 20 weird and scary fish in the water.
Deep Sea Anglerfish
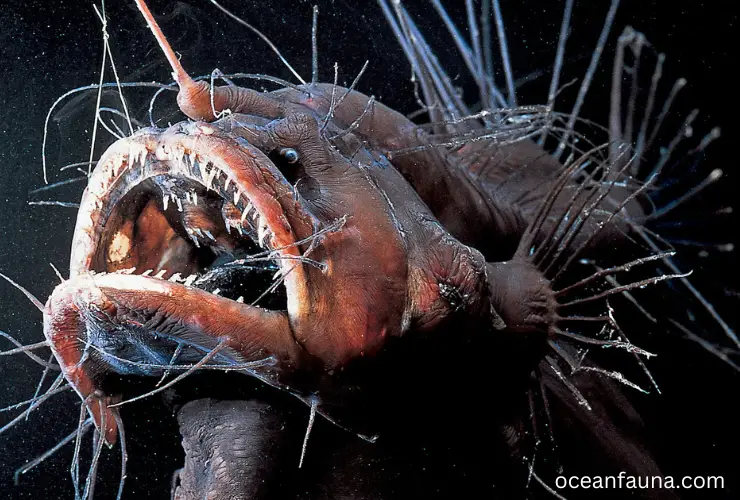

Deep sea anglerfish, also known as Melanocetus johnsonii, is a fascinating yet terrifying creature inhabiting the ocean’s darkest depths. They belong to the family Melanocetidae and the order Lophiiformes. These fish are known for their unique appearance and ability to attract prey in the ocean’s depths.
Deep sea anglerfish are primarily carnivorous, feeding on small crustaceans, squid, and fish. The bioluminescent tip of their dorsal spine acts as a lure, attracting unsuspecting prey to come closer. Once prey is within striking distance, the anglerfish will quickly snap its jaws shut.
These anglerfish are found in the deep ocean, living at depths of up to a mile below the surface. They are often found near the sea floor, blending in with their surroundings to avoid detection.
Deep sea anglerfish can be found in many world regions, primarily in the temperate and tropical regions of the Atlantic and Antarctic Oceans. They prefer to live in areas with low levels of light and high pressure, allowing them to thrive in the deep ocean.
Despite their frightening appearance, deep-sea anglerfish have a relatively docile behavior. They are slow-moving and often remain stationary, waiting for prey to come to them. The females are much larger than the males and are known for absorbing their mate’s body and using their genetic material for reproduction.
Blobfish
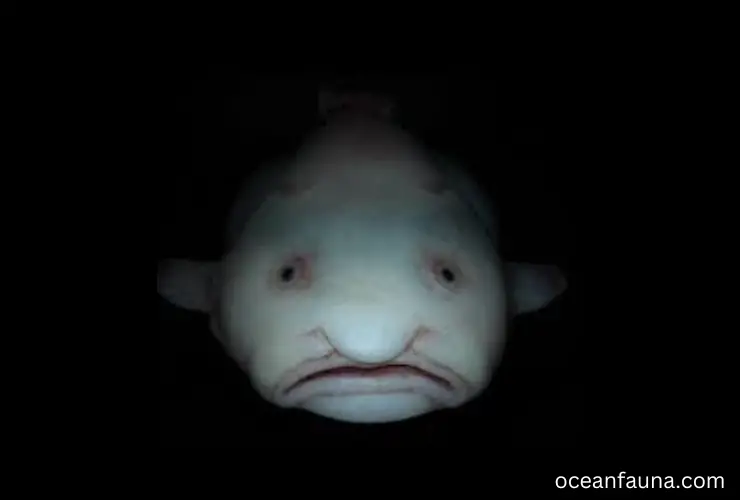

The Blobfish, or Psychrolutes microporos, is a deep sea fish belonging to the family Psychrolutidae and order Scorpaeniformes. In 2013, it earned its place as the world’s ugliest animal.
This strange-looking fish has a gelatinous appearance due to its lack of muscles and bones that would otherwise hold its shape, making it one of the most unusual creatures in the ocean. It is also known as the “Mr. Blobby” of the sea.
The Blobfish has a diet consisting mostly of crustaceans and other deep sea creatures like sea pens and sea urchins. It predominantly resides in the ocean’s deep waters, at depths ranging between 2000-4000 feet, which is its habitat of choice.
The distribution of the Blobfish is limited to a few areas of the world, like the Indo-Pacific and Atlantic oceans. They are not very active creatures and thus have very low metabolic rates. Due to their lack of motion, they are able to conserve energy, which is a crucial tactic considering the deep-sea environment they inhabit. They spend most of their time sitting on the ocean floor, immobile and waiting for prey to swim by.
Frilled Shark
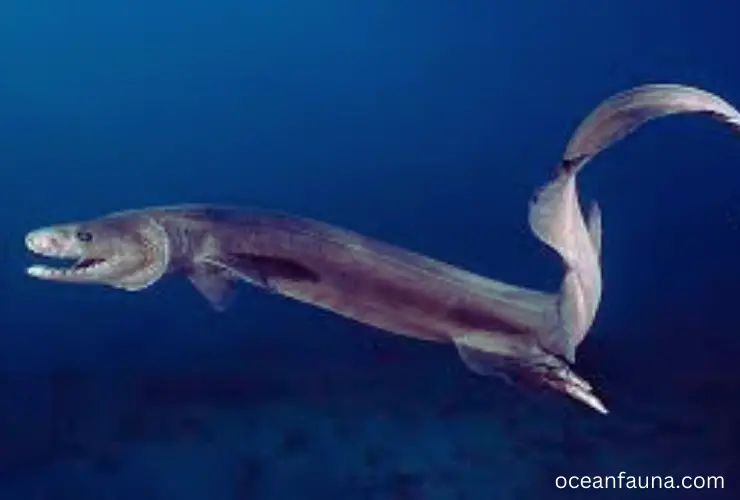

The Frilled shark, also known as Chlamydoselachus anguineus, is a species of deep-sea shark that belongs to the family Chlamydoselachidae and the order Hexanchiformes. This shark measures around 7 feet in length and has a unique frilled appearance, with six pairs of frilly gill slits that resemble a collar.
The diet of the Frilled Shark consists of squid, bony fish, and other small sharks. Due to its deep-sea dwelling, the Frilled shark can hunt in areas other predators cannot reach. It is known to use its long, snake-like body to ambush its prey and engulf them whole.
The Frilled shark is found in deep-sea habitats throughout the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, at depths of up to 1,000 meters. It is also known to live in submarine canyons and plain abyssal environments.
This species is considered to be one of the most primitive sharks alive today, with a lineage that dates back over 80 million years. In terms of behavior, the Frilled shark is a solitary creature that spends most of its time in the darkness of the deep sea.
Interestingly, females have a prolonged gestation period of up to 3.5 years and give birth to live young instead of laying eggs. The young are born fully developed and can survive on their own immediately after birth.
Monkfish
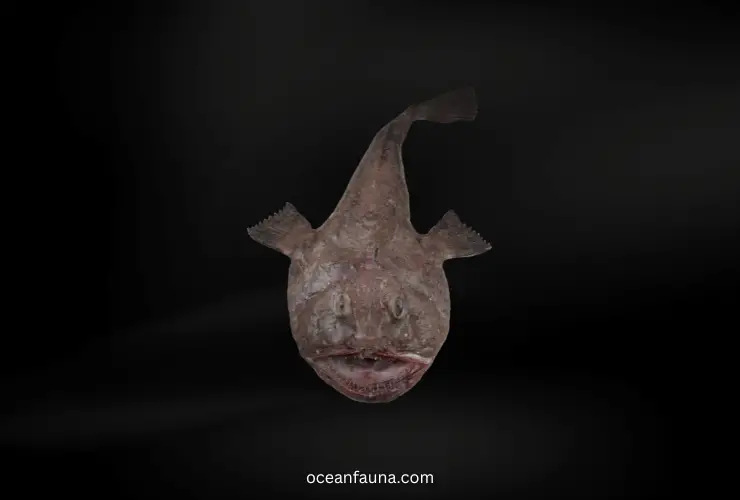

Monkfish belongs to Lophius family. It has a long blob-like body and an extremely wide, flat head that can measure up to two-thirds of its total length.
The diet of the Monkfish consists mostly of other smaller fish, as well as squid, crabs, and even other Monkfish. It has a notorious reputation for being an aggressive predator, using its large mouth to quickly suck in prey items.
Monkfish can be found in the Northwest Atlantic Ocean from shallow coastal waters down to depths of 3000 feet. They are mostly solitary creatures that prefer to stay near the bottom of the ocean floor, waiting in ambush for prey to come within range.
Goblin Shark
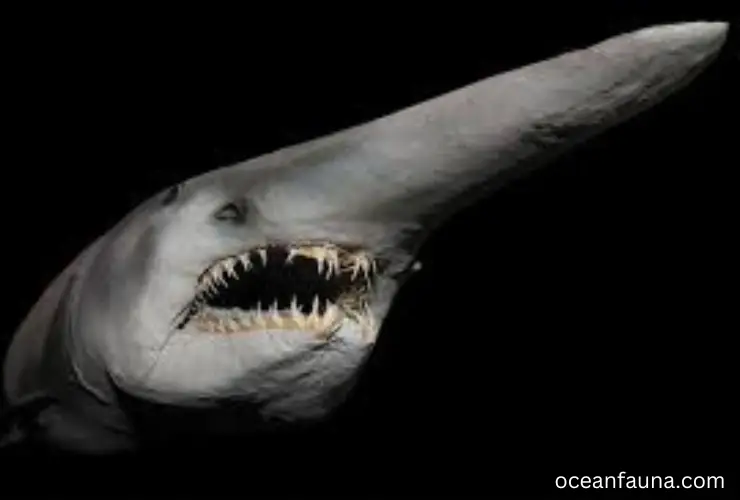

The Goblin Shark, also known as Mitsukurina owstoni, is a rare and unusual species of deep-sea shark that belongs to the family Mitsukurinidae and the order Lamniformes. This shark is named after its bizarre appearance, with a long protruding snout and protrusible jaws that can extend out to capture prey.
As an apex predator, the Goblin Shark feeds on various deep-sea fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods. It uses its protrusible jaws to capture prey by suction, and its sharp teeth are adapted for gripping and slicing. It is known to migrate vertically in the water column, following the distribution of its prey.
The Goblin Shark is found in deep-sea waters around the world, from the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans to the Indian Ocean. It prefers depths of 1,000 to 3,000 feet, although it has been found as deep as 4,265 feet.
Lamprey
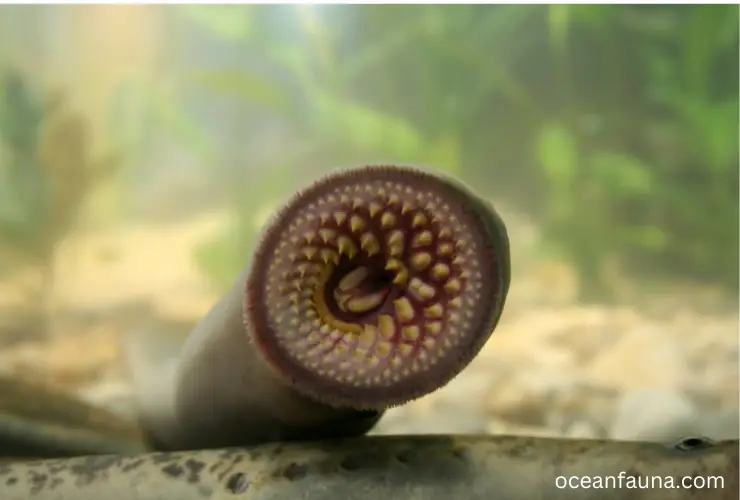

The lamprey is a jawless fish belonging to the family Petromyzontidae and order Petromyzontiformes. Its scientific name is Petromyzon marinus. Lampreys have cylindrical bodies that lack scales and paired fins. Instead of jaws, they possess a sucker-like mouth filled with numerous sharp teeth, which they use to attach themselves to other fish and feed on their blood and body fluids.
Lampreys are found in temperate freshwater and marine environments around the world, including North America, Europe, and parts of Asia. Some species are anadromous, which means they migrate from the ocean into freshwater to spawn.
These carnivorous fish have a varied diet, consisting of other fish, invertebrates, and sometimes even marine mammals. Lampreys have a keen sense of smell, which they use to locate their prey. They can also detect the weak electrical signals produced by other fish, allowing them to locate prey even in complete darkness.
Interestingly, lampreys are often used as model organisms in scientific research due to their unique biological features. They have a primitive immune system, which makes them more susceptible to certain diseases, allowing researchers to study the immune response in greater detail.
Additionally, lampreys have significant regenerative capabilities, making them a valuable subject for studying tissue repair and regeneration.
Dragonfish
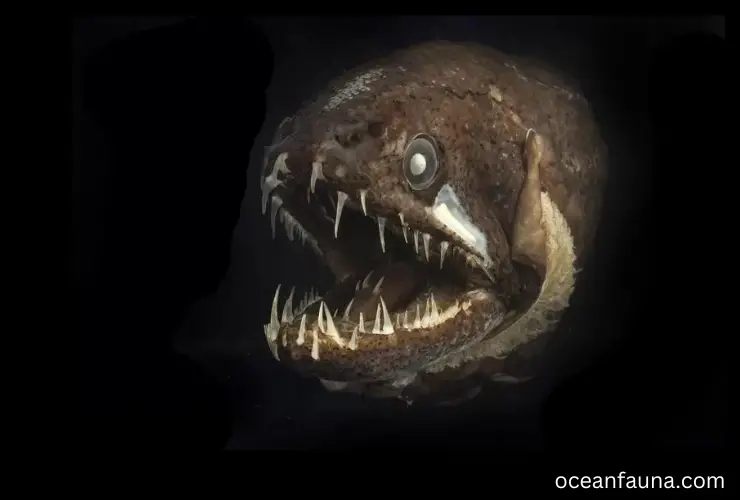

Dragonfish, scientifically known as Pterois, is a tropical marine fish belonging to the family Scorpaenidae and order Scorpaeniformes. These fishes are native to the Eastern Pacific region.
In the wild, Dragonfish are carnivorous predators known for their voracious appetite. They primarily feed on small fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods, using their venomous spines to subdue their prey. Dragonfish has an impressive ability to swallow prey larger than their own body size due to their remarkable flexibility and elastic jaws, which can expand to more than double their original size.
Their potent venomous spines, which are located on their dorsal, anal, and pelvic fins, are used as a defense mechanism against predators. The toxin produced by the glandular tissue surrounding the spines is powerful enough to cause severe pain, swelling, and, in rare cases, even death.
Dragonfish can thrive in various marine environments, from coral reefs to rocky shores, and can be found at depths ranging from 200-1500 meters. They are primarily nocturnal and prefer to hide during the daytime, making them difficult to spot for divers and snorkelers.
Wolf Eel
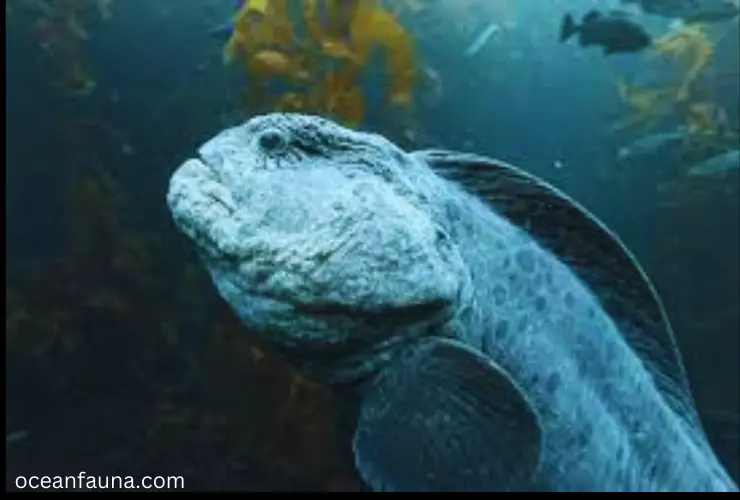

The Wolf Eel, also known as the carpet eel blenny, has the scientific name Anarrhichthys ocellatus. It belongs to the family Anarrhichadidae and the order Perciformes.
Despite its name, the Wolf Eel is not really an eel but rather a type of fish that resembles one due to its elongated body and lack of scales.
The diet of the Wolf Eel consists mainly of crabs, clams, sea urchins, and various other invertebrates. They have a strong set of teeth which they use to crush their prey’s shells.
Wolf Eels can be found in the North Pacific Ocean, from Japan to the Gulf of Alaska, and along the western coast of North America. They are typically found in rocky areas or reefs at depths up to 740 feet.
Hagfish
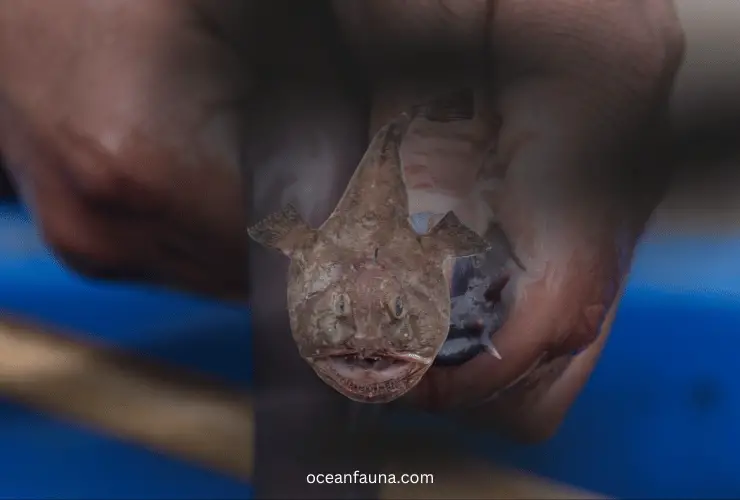
The Hagfish, or Myxine is a marine creature belonging to the family Myxinidae. It has an eel-like body and is known for its ability to produce copious amounts of slime when disturbed.
This slimy species feeds mostly on dead or dying fish, as well as other invertebrates. It has an elongated, snake-like body that is covered in tiny denticles or scales.
The Hagfish can be found in the Pacific oceans at depths of over 4000 feet. They are primarily nocturnal creatures and spend most of their time hiding under rocks during the day.
Hagfish are known for their ability to produce copious amounts of slime when threatened or disturbed. The slimy substance is made up of thick mucus strands that expand exponentially in water, allowing the Hagfish to escape predators by clogging up their gills and mouths.
Fangtooth Fish
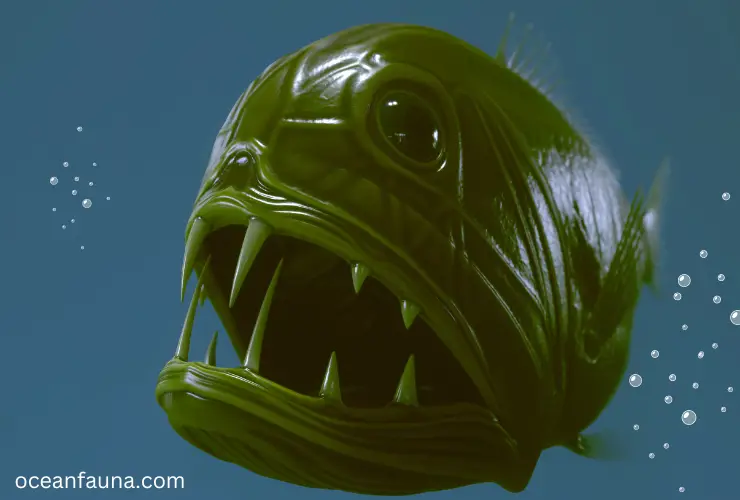

Anoplogastridae and the order Beryciformes. These fish are typically found in deep ocean waters, usually between 500 and 2,000 meters below the surface.
Despite their name, fangtooth fish don’t actually have fangs. Instead, their teeth are long and needle-like, and they are the largest teeth in comparison to the body size of any known fish species. These teeth are used to catch and hold onto their prey, which is largely composed of small fish and crustaceans.
Apart from their unique teeth, fangtooth fish also possess other distinct physical features. They have large eyes that help them navigate the darkness, and their bodies are covered with scales that can change color depending on the situation.
Fangtooth fish are widespread and found in all the major oceanic areas, including the Atlantic, Indian, and Pacific Oceans. They are most commonly found around islands, seamounts, and ridges. Due to their deepwater habitat, these fish are less impacted by human activities, making them less vulnerable to overfishing.
Barreleye Fish

The Barreleye fish, also known as Macropinna microstoma, belongs to the Opisthoproctidae family and the Osmeriformes order. This unique-looking fish is often recognized for its highly-domed transparent head enclosing its eyes. These eyes can rotate within their protective casing, allowing the Barreleye to see directly upwards, downwards, and forwards.
Recent research has shown that the Barreleye’s large, telescope-like eyes also contain green pigment, which may filter out sunlight and enhance the fish’s ability to detect bioluminescent signals from other deep-sea creatures. Despite its peculiar appearance, this fish is considered a fierce predator at depths of up to 2600 feet, where it feeds on small zooplankton and jellyfish that drift by.
The Barreleye fish is mostly found in the deep, dark waters of the Pacific Ocean, specifically off the coast of California and Japan.
Viperfish

The Viperfish, scientific name Chauliodus sloani, belongs to the family Stomiidae and order Stomiiformes. This deep-sea predator can grow up to 30 centimeters long and uniquely appears due to its fang-like teeth, elongated body, and long dorsal fin ray.
Viperfish are carnivorous and feed on smaller fish, crustaceans, and squid. They use their bioluminescent photophores to attract prey and have been known to swim at depths of up to 9000 feet in the ocean.
These fish are found only in the Pacific Ocean. Viperfish are known for their ability to survive in extreme conditions, including cold temperatures and high pressures.
Unlike some other deep-sea fish, Viperfish are not commercially fished due to their small size and limited distribution. However, they are sometimes caught accidentally in deep-sea trawls. These fish are essential to the ecosystem as they serve as prey for larger fish and play a vital role in the food chain.
Coffinfish
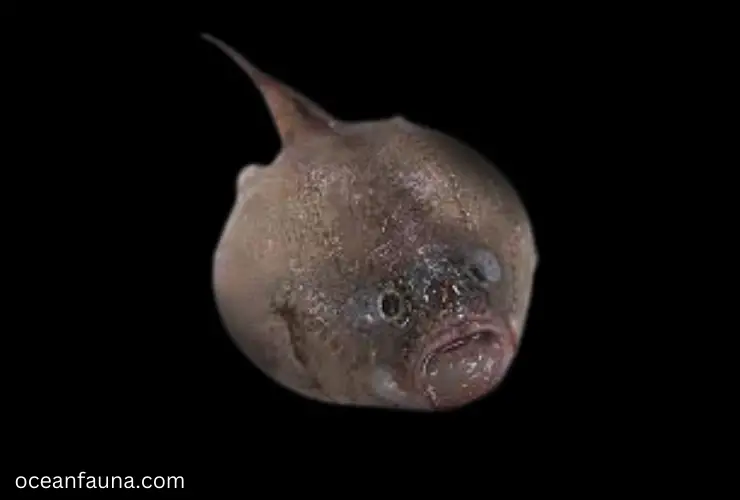

The Coffinfish, scientifically known as Chaunax endeavouri, is a species of anglerfish belonging to the family Chaunacidae and the order Lophiiformes. They have a unique appearance with their flattened, wide head and small, stalked eyes. Their body is covered in a layer of slime, and they have a lure at the tip of their snout to attract prey.
Coffinfish is found in deep waters throughout the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, ranging from 180-1100 meters deep. They prefer muddy or sandy bottoms where they can hide and ambush their prey. Their diet primarily consists of small fish and crustaceans, which they catch using their lure and quickly swallow whole due to their large expandable stomach.
One interesting fact about Coffinfish is that they can inflate their body like a balloon to deter predators. They also have a specialized organ in their body that produces light, which they use to attract prey in the darkness of the deep ocean.
Stargazer Fish

Stargazer fish, also known as Uranoscopidae, are a family of perciform fish that are known for their unique appearance and predatory habits. Their scientific name, Uranoscopidae, comes from the Greek words “ouranos,” which means “sky,” and “skopein,” which means “to look at,” due to their upward-facing eyes.
Stargazers are typically found in shallow waters of up to 120 feet deep throughout tropical and temperate regions of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Some species can also be found in deep-sea habitats, up to 500 feet deep.
These fish are ambush predators and have adapted to bury themselves in the sand or mud to hide and wait for prey to come closer. They have a large, upward-facing mouth that allows them to catch small fish, crabs, and other invertebrates that are swimming above them.
Stargazers have a compressed body shape, with a round head and a tapering body that ends in a small tail. Their eyes are located on top of their head, which allows them to keep an eye on their surroundings while buried in the sand.
Stonefish
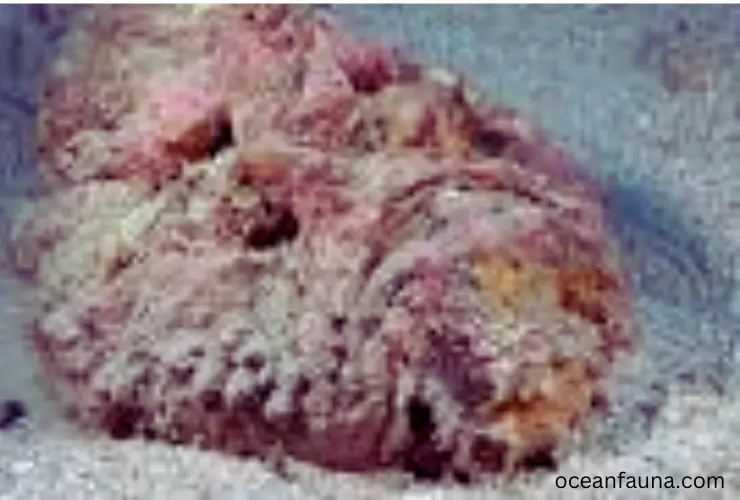
The Stonefish, also known as Synanceia, belongs to the family Synanceiidae, and the order Scorpaeniformes. This is one of the most venomous fish in the world, and its sting can be fatal to humans if not treated on time.
Stonefish are primarily carnivores, and their diet consists mostly of small fish and crustaceans. They are typically found in the coastal regions of the Indo-Pacific, from the Red Sea to the Pacific Ocean. These fish inhabit shallow waters, especially reef areas and coral reefs.
Most Stonefish species are well-camouflaged and can blend perfectly with their surroundings, making them hard to spot. They have spines on their dorsal fins, which they erect when threatened, making them look like stones, hence their name.
The venom of the Stonefish is contained in its dorsal spines and can remain deadly even after the fish has died. Coming into contact with the spines can cause severe pain, tissue damage, paralysis, and even death in some cases. Antivenom is the best solution for a sting from a Stonefish, and immediate medical attention is necessary.
Lionfish
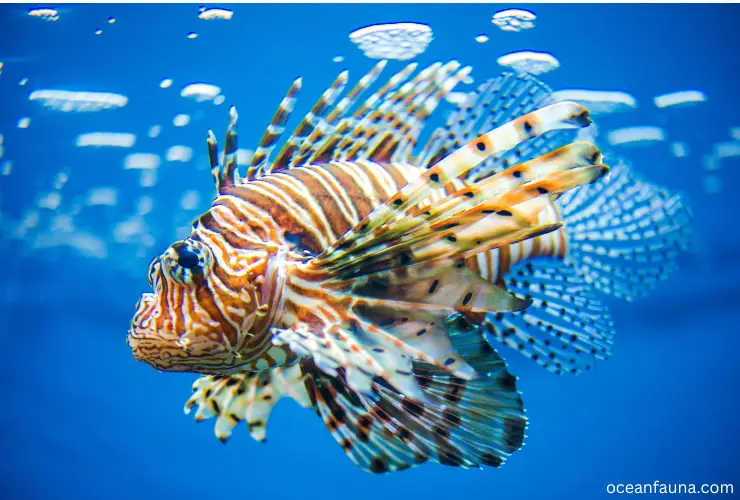

The lionfish, scientifically known as Pterois volitans, belongs to the family Scorpaenidae and the order Scorpaeniformes. This venomous fish is native to the South Pacific and Indo-Pacific region but has become an invasive species in the Atlantic Ocean due to aquarium releases and accidental escapes from breeding facilities.
The lionfish is known for its striking appearance, with flamboyant red, orange, and white stripes on its body, long flowing fins, and venomous spines that protrude from its back. These spines, which are used for defense against predators, can cause intense pain, swelling, and even death in humans.
Lionfish are carnivorous and feed primarily on small fish and invertebrates. They have been known to consume up to 30 different species of prey. Their distribution is vast, ranging from coastal areas to deep reefs, and they can be found at depths of up to 300 meters.
Moray Eel
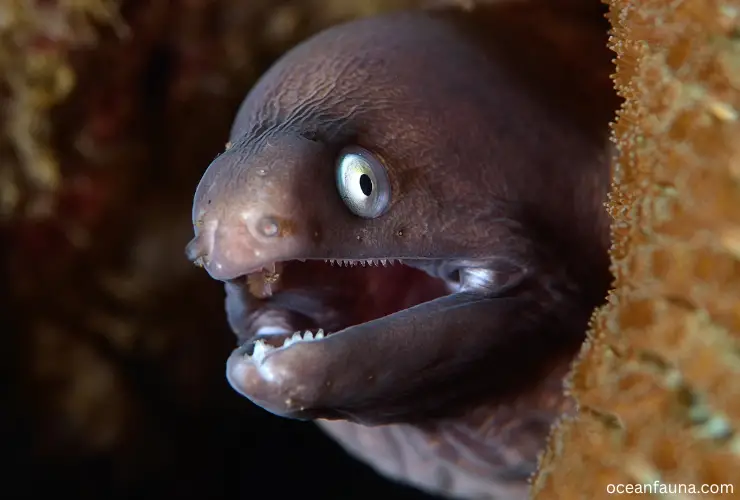

The Moray Eel is a type of fish belonging to the family Muraenidae, and its scientific name is Gymnothorax. These eels are commonly found in tropical and subtropical waters of the Mediterranean Sea and Northeast Atlantic. They are known for their long, slender bodies and snake-like appearance, with some species growing up to 11.5 feet in length.
Moray Eels are carnivorous creatures that feed on marine animals, including fish, shrimp, and squid. They have a powerful jaws filled with sharp teeth, which they use to catch and crush their prey. Additionally, some species of moray eels also have venomous bites, which they use to defend themselves against predators.
One interesting fact about the Moray Eel is that they can breathe through their skin in addition to their gills. This adaptation helps them survive in areas with low oxygen levels, such as coral reefs and rocky crevices. Moray eels are also known for their unusual reproduction habits, with fertilization occurring in the water column rather than internally.
Scorpionfish

The Scorpionfish, scientific name Scorpaena scrofa, belongs to the family Scorpaenidae and the order Scorpaeniformes. This fish is commonly found South Pacific and Indian Oceans.
The Scorpionfish has a distinctive appearance, with colorful markings and spines on its body. This fish has a carnivorous diet, feeding on small fish, crustaceans, and other marine invertebrates. It is known for its venomous spines, which it uses as a defense mechanism against predators.
Interestingly, the Scorpionfish has adapted to its environment by being able to camouflage itself, blending in with its surroundings to ambush prey. It also has a unique hunting technique where it stays motionless and uses the current to bring food to it.
With its venomous spines, the Scorpionfish is a dangerous fish to handle and can often result in painful stings if not handled with care. Despite its venomous spines, the Scorpionfish is considered a delicacy in many parts of the world and is commonly used in sushi and other seafood dishes.
Sarcastic Fringehead
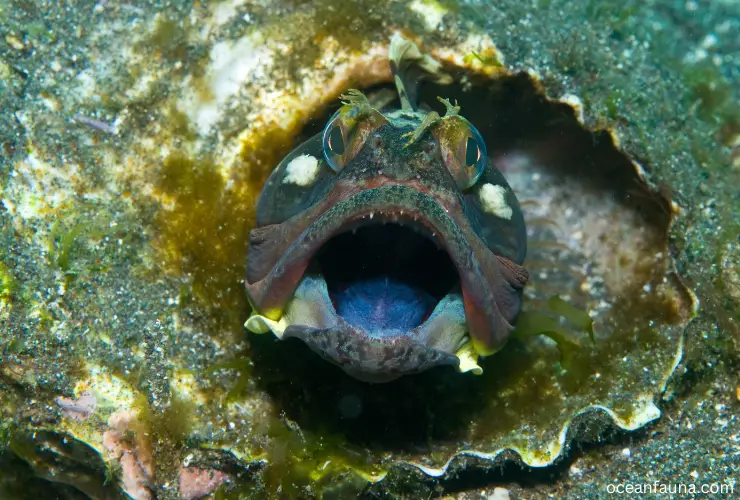

The Sarcastic Fringehead, scientifically known as Neoclinus blanchardi, is a species of fish that belongs to the family Clinidae and the order Perciformes. Found in the Pacific Ocean from San Francisco Bay to Mexico, these fish are typically found in rocky reefs and tide pools at depths ranging from 3 to 61 meters.
The Sarcastic Fringehead, known for its unusual physical appearance, has a large head with a comically wide mouth that extends beyond the eyes. It has a brightly-colored body with a mottled pattern of yellow, orange, and red and distinctive fringed tentacles above its eyes that it displays during aggressive displays.
These fish are primarily carnivorous, feeding on various small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks. They are known for their aggressive behavior and will fight fiercely over territory and potential mates. Male Sarcastic Fringeheads guard and tend to the eggs until they hatch, which takes approximately six weeks.
In addition to its unique appearance and aggressive behavior, the Sarcastic Fringehead has a highly developed lateral line system that enables it to detect vibrations and changes in the water. This allows them to navigate through rocky reefs and detect prey even in low-light conditions.
Goblinfish
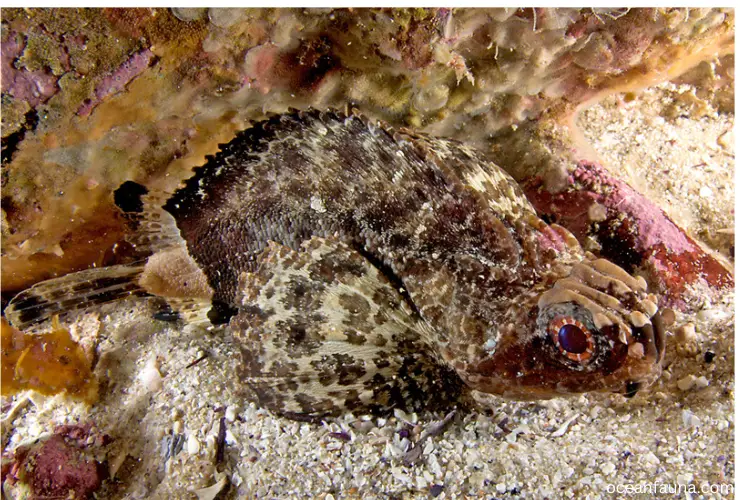

The Goblinfish also known as the Glyptauchen panduratus, belongs to the family of Cottidae and the order of Scorpaeniformes. This species of fish has a unique appearance with its large head, bulging eyes, and broad mouth with sharp teeth.
The Goblinfish is a carnivorous species that feeds on small fish, crabs, and shrimps. They use their wide mouth to capture prey and have been known to swallow whole fishes larger than themselves.
Endemic to Australian waters, the fascinating Goblinfish inhabits shallow marine habitats ranging from rocky terrain to sandy seabeds up to 22 meters deep.
The Goblinfish’s fascinating adaptation helps them blend in with their surroundings. They can change their color to mimic their background, making it easier for them to avoid predators or ambush their prey.
Conclusion
Hopefully, you have enjoyed this article knowing about the 20 scariest and weirdest fish. Although these fish have distinct characteristics and appearances, they all share the common trait of being able to survive in their respective environments.
From the venomous Scorpionfish to the color-changing Goblinfish, these strange creatures are a testament to the beauty and diversity of our oceans.

