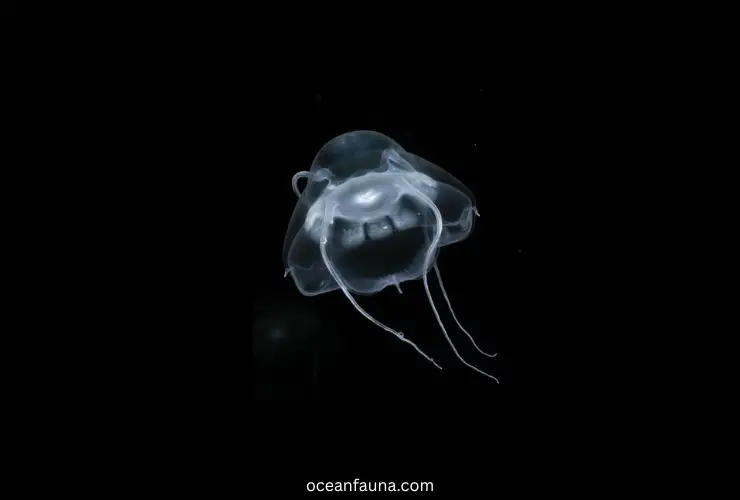
Narcomedusae jellyfish are counted as part of the Cnidarian family. You can find them in oceans worldwide, especially in deep waters and the open sea. They have beautiful bell-shaped bodies and vary in size.
Furthermore, narcomedusae jellies have a unique way of feeding. They do not possess a mouth or digestive system. They trap their food in mucus, transport it to their oral arms, and digest it. They trap plankton and small organisms. These are undoubtedly wonders of the oceans.
Have you ever thought about how they survive in the oceans? Do you have curiosity about how they reproduce? These are crucial components of the ecosystem.
That’s why we are here to unfold secrets about the life of Narcomedusae Jellyfish. So, grab a coffee mug and keep reading. We are about to discover more fascinating facts about it.
About Narcomedusae Jellyfish – A Quick Biology
We have created a quick biology table for your ease so that you can have an eye over these facts too. Hope you like these important facts about these jiggly marine animals.
| Parameters | Details |
| Scientific name | Narcomedusidae |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Families | Tetraplatidae, Solmarisidae, Cuninidae, Aeginidae, Csiromedusidae, Pseudaeginidae, Solmundaeginidae |
| Genus | Narcomedusae |
| Phylum | Cnidaria |
| Class | Hydrozoa |
| Order | Narcomedusae (Haeckel, 1879) |
| Species | Aeginura Grimaldi, Solmissus albescens, Solmissus incisa, Solmissus octothecatus, Solmissus squamulatus, and more. |
| Habitat | Deep-sea environments, continental slopes, shallow waters of coral reefs |
| Life Span | Six months or less than one year |
| Diet | Small plankton organisms and small crustaceans |
| Geographical range | From the Arctic to the Antarctic oceans, including all major oceans. |
Some Amazing Fun Facts about Narcomedusae Jellyfish
Here are some fun facts about these remarkable species of jellyfish:
- Narcomedusae jellyfish are also known as stalked jellyfish. This name was given to them due to their unique morphology.
- There are more than 50 known species of narcomedusae jellies.
- Narcomedusae jellies have the ability to filter food that they have caught as prey. They do this by pumping water through their bell.
- These species of jellyfish do not have bones, muscles, and other major organs.
- These sea creatures are capable of regenerating their lost body parts. This is quite a surprising fact about them.
- Some species of narcomedusae jellyfish have a complex life cycle. They reproduce sexually and asexually.
- These sea jellies can be found under 4,000 meters. This is a lot of depth.
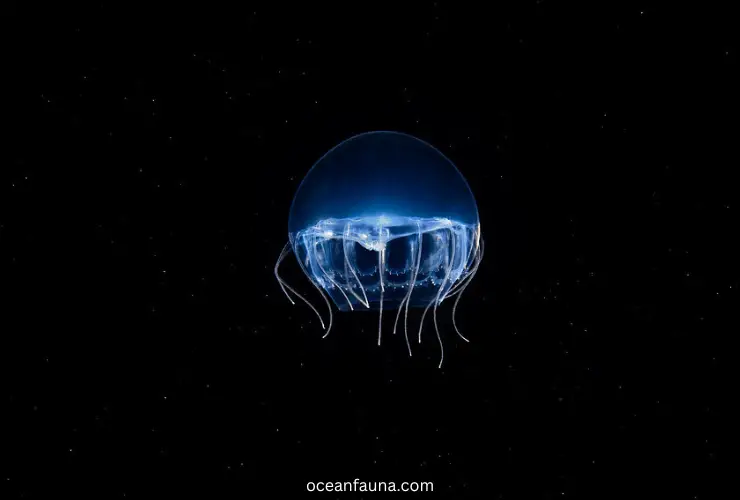

Description And Distribution of Narcomedusae Jellyfish
The order of narcomedusae jellyfish are hydrozoans. It belongs to the subclass of Trachylinae. The jellies of this member have something unique in their reproductive system. They skip the polyp stage.
Yeah, it’s a fact that makes them different from other species of sea jellies. The medusa of narcomedusae sea jellies has thin sides. It’s basically a dome-shaped bell. The tentacles are situated above the lobed edge of their bell-shaped body. This is quite worth mentioning!
Typically, there is a gastric pouch located above each tentacle. This unique arrangement enables these jellyfish to capture and digest their prey efficiently. These sea jellies do not have radial canals and bulbs on their tentacles.
Now, let’s go to the section on its distribution. It’s distributed all over the world. Moreover, these species of jellyfish lives in open waters and deep oceans. These are also distributed in shallow waters of oceans worldwide. They live near coral reefs.
Anatomy / Appearance of Narcomedusae Jellyfish
Narcomedusae jellyfish have a bell-shaped body with beautiful tentacles like other sea jellies. This is something to be mentioned first. Moreover, its size varies from a few millimeters to several centimeters in length.
Thus, narcomedusans have complex anatomy. These marvelous jellies have several distinct physical characteristics:
- Umbrella: Narcomedusae Jellyfish have bell-shaped bodies like umbrellas. This body shape helps them swim easily and propulsively move in the water. It is made up of transparent and flexible membranes. Muscle fibers surround their bodies.
- Tentacles: Narcomedusae jellyfish have thin but long tentacles. As we have mentioned before these are used for capturing prey. The stinging cells are covering these tentacles.
These stinging cells are commonly called nematocysts. These cells help them to immobilize their prey without any further delay.
- Oral arms: The first and foremost question that arrives in our minds is, what are these oral arms? These are the thin and long extensions of the body of narcomedusae jellyfish.
These sea creatures use oral arms for feeding purposes. The oral arms are lined with cilia. Cilia is a small hair-like structure that helps the jellyfish to move food particles toward its mouth.
- The mouth of Narcomedusae Jellyfish: Its mouth is located at the base of its oral arms. These sea jellies use their mouth for the ingestion of food.
- Gonads: Narcomedusae sea jellies have gonads located in their umbrella-shaped bodies. They are either male or female. The gonads are their separate reproductive organs.
- Exumbrella: The outer surface of the Narcomedusae Jellyfish is known as an exumbrella. It faces away from its body.
Overall, the anatomy of Narcomedusae Jellyfish is unique and complex. It enables them to live happily, survive in tough conditions, and thrive in aquatic environments.
Behaviors of Narcomedusae Jellyfish
Narcomedusae jellyfish have many unique and intriguing behaviors. Let’s discuss a few of them below.
Feeding Behavior
According to the research article of Cambridge University Press, Narcomedusae jellyfish have an interesting feeding behavior. Let’s see what they say about this behavior-
“Narcomedusae jellyfish capture swift prey with their tentacles. They hold their tentacles perpendicular to their swimming direction, expanding their reach. When prey is caught, the tentacle tips coil inwards, and the jellyfish consumes it.
They use this tactic to hunt in the depths of the ocean. Due to the scarcity of food in the deep sea, they have adapted to hunt larger prey by using their long and flexible tentacles. This is something interesting about these narcomedusae Jellyfish.”
Swimming Behaviour
The species of narcomedusae are commonly called free-swimming creatures. They have this common behavior. These jellies use a pulsating motion in order to move through the water.
This behavior helps them to move freely in deep-sea waters and harsh environments. The extreme conditions of the deep sea include high pressures and cold temperatures. So, this free-swimming behavior helps them to survive.
Defense Behavior
As mentioned, narcomedusae jellyfish have stinging cells to catch and immobilize prey. These cuddly creatures also use these nematocysts as a defense mechanism. They protect them from predators by using their stings.
Their defense mechanism does not just base on stings. They can also release bioluminescent chemicals. It means they produce light. They release these chemicals not just to attract prey but also startle predators. Thus, narcomedusae jellyfish are intelligent and defensive.
Vertical Migration Behavior
Some species of narcomedusae jellyfish have vertical migration behavior. It means they move vertically in the water column over a day.
They stay in deeper waters in the ocean during daylight and move toward the surface at night for feeding purposes. This behavior also helps them to survive in the wild regions of seas and oceans.
Habitat And Range of Narcomedusae Jellyfish
Narcomedusae Jellyfish are commonly known and described as deep-sea species of jellyfish. It is known that the Mediterranean is the best place for these inhabitants. Narco Medusans are in larger quantities in the Mediterranean ocean than any other.
The range of narcomedusans is not understood well because these live in deep oceans. However, according to a study, their habitat and range are from the Arctic to the Antarctic oceans. It also includes any other major oceans in between them, like the Indian Ocean.
Narcomedusae jellyfish are usually associated with cold seeps and deep-sea hydrothermal vents. These are areas on the floor of oceans where gasses and hot water are released from the crust of the Earth. This is quite a surprising fact.
These deep-sea areas are rich in nutrients and diversity of life along with unique habitats for deep-sea species of jellies and other creatures. Overall, these chubby creatures are adapted to live in harsh environments like deep-depth oceans, high temperatures, and sparsely distributed food.
Feeding / Diet of Narcomedusae Jellyfish
Narcomedusae jellyfish are opportunistic feeders. These marine animals eat small animals. These are carnivorous and love to eat small planktonic animals like copepods, krills, and small crustaceans.
According to the Arctic Ocean Diversity organization’s researchers, the species “Aeginopsis laurentii” feed on other gelatinous taxa. Thus, their specific diet depends on the specific species of narcomedusae. (Source)
The Narcomedusae Jellyfish are also feeding on small fish. They capture their prey using their oral arms and tentacles. Other small marine organisms and small jellyfish are also the prey of narcomedusans.
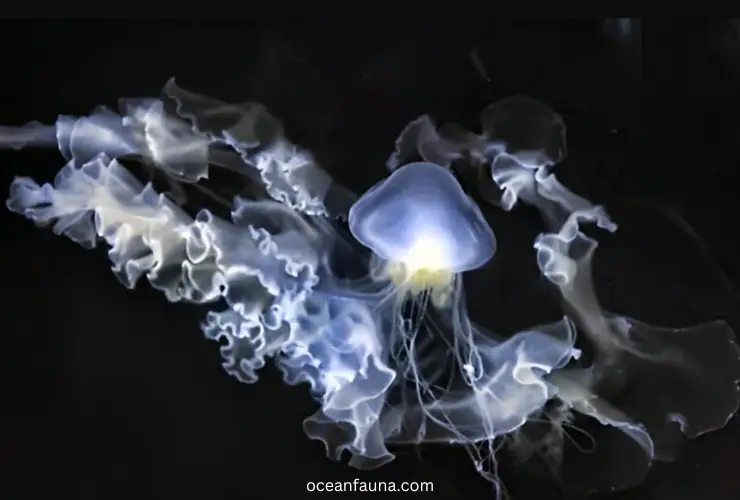

Life Cycle And Reproduction System of Narcomedusae Jellyfish
The life cycle and reproduction system of Narcomedusae Jellyfish is a little bit complex compared to other sea jellies. Narcomedusans are hermaphroditic. It means they have both male and female organs of reproduction.
They reproduce sexually. But, how? Let’s discuss it below and see what the Marine Biology research paper has found about its reductive cycle-
“Narcomedusae jellyfish reproduce sexually when males release their sperm in the water. On the other hand, females release their eggs in the water too. Here, fertilization occurs externally in the water column.
Now, planula larvae will be formed after the development of fertilized eggs. Planula is also known as the larval stage. The planula larvae will then live in the seabed/seafloor.
Here they go through the metamorphosis stage and then bud off small jellyfish. These small jellies are known as Ephyrae. At the last stage, the ephyrae developed into an adult jellyfish eventually.”
So, this is how the greatest Narcomedusae Jellyfish reproduce. Its life cycle begins with the reproduction and fertilization process, develops into free-swimming larvae, settles on the seabed, and becomes an adult jellyfish.
As far as its lifespan is concerned, the age range is not specified or researched before. However, these sea jellies are believed to live only 6 months to less than a year more.
Their lifecycle and reproductive system are important to understand for finding the ecology of these creatures. These have flexible mating behavior and more successful reproduction chances in harsh environments.
Cardiovascular And Nervous System of Narcomedusae Jellyfish
Here is everything that you should know about the cardiovascular and nervous systems of Narcomedusae Jellyfish:
Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system of Narcomedusae Jellyfish is really simple compared to other animals. They have an open circulatory system. Yeah! Their blood is not confined to a closed network of blood vessels.
Instead, their blood flows freely throughout their bodies’ coelenteron or body cavity. It is then surrounded by a muscular layer called the mesoglea. Thus, these sea creatures do not have a heart or blood vessels to pump blood throughout their bodies.
Instead, their blood is pumped throughout the body by contraction of their muscular bell. This bell creates a pumping action that helps them not just circulate blood but also distribute nutrients and oxygen to all tissues of the body.
Nervous System
The nervous system of narcomedusae jellyfish is also very simple, like the cardiovascular system. It is decentralized throughout their body. They do not possess a centralized brain or centralized ganglia.
Instead, they have a network of nerves all over their tentacles and bell. It is spread throughout their body. This nerve net consists of interconnected neurons. These neurons can be used to detect and react to various stimuli like chemicals, light, and touch in the water.
Importance of Narcomedusae Jellyfish in the Ecosystem
Narcomedusae jellies play a vital role in the ecosystem. These marine animals have significant impacts on the communities they inhabit. They are contributing to the ecosystem in the following ways:
Trophic Interactions
Narcomedusae jellyfish are amazingly interesting in the way of trophic interactions. These are predators that eat small planktonic animals. In this way, they consume these animals and regulate their populations of these animals. It helps them to control the flow of energy through the food web.
Nutrient Cycling
These weird creatures produce a large quantity of mucus and waste in their lifespan. This waste serves as a source of nutrients for many other organisms in the water. It helps to fuel the growth of other microorganisms and bacteria. In turn, these organisms support higher trophic levels.
Predators of Narcomedusae Jellyfish
There are many predators of the species of Narcomedusae Jellyfish. Some predators may include the following:
| Predators | Details |
| Deep-Sea Fish | Dragonfish (Stomiiformes), lanternfish (Myctophiformes), and many other species of fish |
| Crustaceans | Amphipods and mysids |
| Other jellyfish | Deep-sea cross jellyfish (Staurophora mertensii) and many other big-sized jellies |
| Squids | Vampire squid (Vampyroteuthis infernalis), the giant squid (Architeuthis dux) |
Relationship between Narcomedusae Jellyfish And Humans
We have mentioned before that narco medusas are deep-sea habitats. So, there is little interaction between humans and Narcomedusae Jellyfish. These are known to have no direct impact on humans. In other words, these are rarely encountered by humans.
However, the activities of humans can impact their surroundings and living standards. Fishing, pollution, and mining are examples of those activities that can impact these marine species negatively.
Does a Narcomedusae Jellyfish Sting Hurt?
Yes. The sting of a narcomedusae jellyfish can hurt mild to moderate if they sting any human or animal. The severity of their stings depends on various factors that include:
- Sensitivity of the skin of the victim
- Size of the species of narcomedusae jellyfish
- Species of the Narcomedusae Jellyfish
If we talk generally about these stinging creatures, they can cause mild effects of their stings like a rash or mild tingling sensation. The moderate effects may include cough, rashes, inflammation, swelling, chest pain, and breathing difficulty.
The sting can also be severe and can cause severe pain and even death in many cases. So, whenever you or someone around you is stung by Narcomedusae Jellyfish, seek medical help immediately.
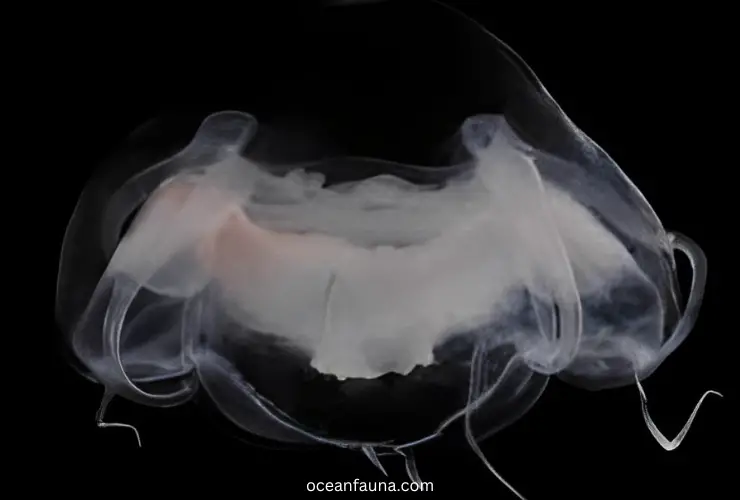
Are Narcomedusae Jellyfish Rare Or Endangered?
The species of narcomedusae jellyfish are neither rare nor endangered. Actually, their population size is unknown and there is little information about their population or conservation status.
However, their population can be impacted by human activities like pollution and climate change. Still, these species of narcomedusae jellyfish can even live in disturbed environments.
The New Jellyfish Found in the Order of Narcomedusae!
More and more research is taking place every day about these jiggly marine animals. Scientists from the NOAA Ocean Explorer program have discovered a new species of jellyfish that falls under the order of narcomedusae. The research took place in 2005 in the Arctic Ocean. (Source)
This jellyfish was found at a depth of 2,000 meters. A remotely operated vehicle was used to collect the samples of jellyfish. This jellyfish was found to have a distinctive body shape and thin tentacles. They have found the following breathtaking anatomy about this species.
They found that this specie of Narcomedusae has the following features:
- Four tentacles
- Twelve stomach pouches
- Four small secondary tentacles
The smaller and secondary tentacles were present at the edge of the bell. Overall, these researchers have evolved our understanding of these cute creatures.
Here is another research from BioTaxa organization that found an amazingly beautiful species of narcomedusae. This species was named as Bathykorus bouilloni. It was observed around 425 times in the depth range between 1,400 to 2,000 meters at eleven stations.
FAQs
How old is narcomedusae jellyfish?
We have stated before that narcomedusae jellyfish are not a specific kind of type of jellyfish. It’s a subclass of jellyfish that includes different species of jellyfish. Each species of jellyfish has its lifespan.
However, most species have a relatively short lifespan of a few months. On the other hand, there are some species of jellyfish that live for much longer lifespans. Immortal jellyfish (Turritopsis dohrnii) is one example of it.
How big is the Narcomedusae Jellyfish?
The size of the Narcomedusae jellyfish depends on the species of the jellyfish. Some species are smaller in size and have only a few millimeters of diameter. However, some species are larger up to 30 centimeters in diameter.
One example of a larger species of narcomedusae jellyfish is Aeginopsis laurentii. Its diameter is up to 20 to 30 centimeters and the tentacles’ length is up to 2 meters. The size of Narcomedusae Jellyfish depends on various factors like environmental conditions, food availability, and age. (Source)
Are Narcomedusae Jellyfish poisonous?
Yes, narcomedusae jellyfish are poisonous. They have poisonous-filled stinging cells. These are present at the end of their tentacles. These stinging cells are harmful to humans and other creatures. They can leave a rash on the stung spot and cause many other complex reactions in the body of the victim.
So, whenever you encountered a narcomedusae jellyfish, just try to stay away from these species of sea jellies. They look beautiful but their stinging cells can hurt you badly sometimes. Immediately seek medical assistance if you are stung by these aquatic animals.
Conclusion
The species of narcomedusae jellyfish are poorly known, but these are the wonders of the sea life. Well, we have almost talked about all the biographical facts about these unique sea jellies. These jellies have fabulous features and they know how to keep us on our toes due to their stings.
Hope you enjoyed reading the fun facts about these mysterious species of jellyfish. Still, if you have any queries pop up in your mind, you can ask us. We would be happy to answer that.

