In short, blobfish don’t have strong bones. All they have is soft cartilaginous structures that support their body weight in the high water pressure of their deep-sea environment.
Blobfish are also known to lack a swim bladder which helps many other fish maintain buoyancy and stay afloat. This means that they have to rely solely on these soft cartilaginous structures rather than bones for support.
To know more about the skeletal system of blobfish, go through this article.
Skeletal System of Blobfish
The skeletal system of blobfish is a unique adaptation to their deep-sea environment. The lack of strong bones is compensated by soft cartilaginous structures supporting their body weight under high water pressure.
Compared to other fish species, blobfish also lack a swim bladder, which makes them dependent solely on their cartilaginous structures for buoyancy and movement.
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that is commonly found in the human body, particularly in joints, ears, and noses. In blobfish, cartilage serves as the primary structural support for their body. This type of tissue offers several advantages over bone.
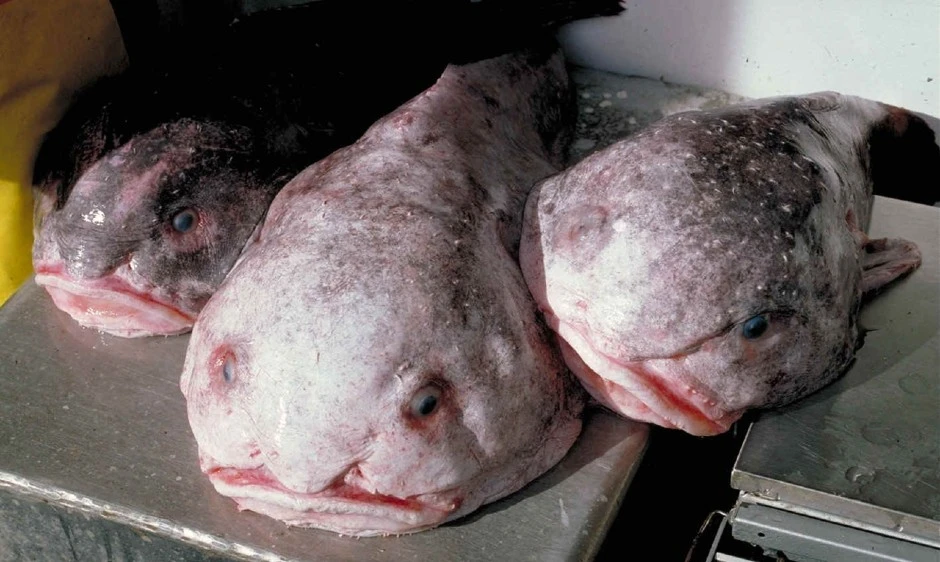

For instance, cartilage is more durable and flexible, which allows it to withstand the enormous pressure of the deep-sea environment. Additionally, cartilage flexibility enables blobfish to move more efficiently and minimize energy expenditure compared to fish with heavy bone structures.
The lack of a swim bladder also contributes to the morphological features of blobfish. The swim bladder is an organ that enables fish to adjust their buoyancy and stay afloat.
Also Read: Are Blobfish Endangered? [How Many Blobfish Left]
However, in deep-sea environments with high water pressure, the swim bladder is not as effective. Therefore, blobfish have evolved without this organ and have adapted to the high pressures of their environment by developing a gelatinous body.
With all these unique adaptations, blobfish have become well-suited to their deep-sea habitat. Their soft cartilaginous structures and gelatinous body shape allow them to move and traverse through the deep-sea environment easily without needing heavy bones or swim bladders.
These adaptations have made the blobfish distinctive and one of the most interesting creatures inhabiting the deep-sea ecosystem.
Why Doesn’t a Blobfish Have Bones?
The blobfish, scientifically known as Psychrolutes Marcus, is a deep-sea creature that lives at a depth of 2,000 to 4,000 feet under the ocean surface.
One surprising fact about the blobfish is that it has no bones but only a cartilaginous skeleton that supports its body. This makes us wonder why the blobfish lacks bones and how it is still able to survive in its harsh, deep-sea environment.
The reason why the blobfish has no bones is most likely due to the low levels of calcium in the deep sea. Calcium is an essential mineral needed for developing and maintaining bones in most vertebrates, including humans.
However, calcium is scarce in the deep sea, and the blobfish has adapted to this low-calcium environment by having a cartilaginous structure instead of bones.
Cartilage is a strong yet flexible connective tissue that is made up of collagen and elastin fibers. It is found in various body parts, including the nose, ears, and joints. Cartilage provides support and flexibility to the body, and it can withstand the pressure and weight of the deep-sea environment much better than bones can.
In addition, having a cartilaginous structure also enables the blobfish to float effortlessly in the water. Unlike bones, which can be heavy and dense, cartilage is more buoyant and helps the blobfish stay afloat without expending much energy.
Do Blobfish Have Any Muscles?
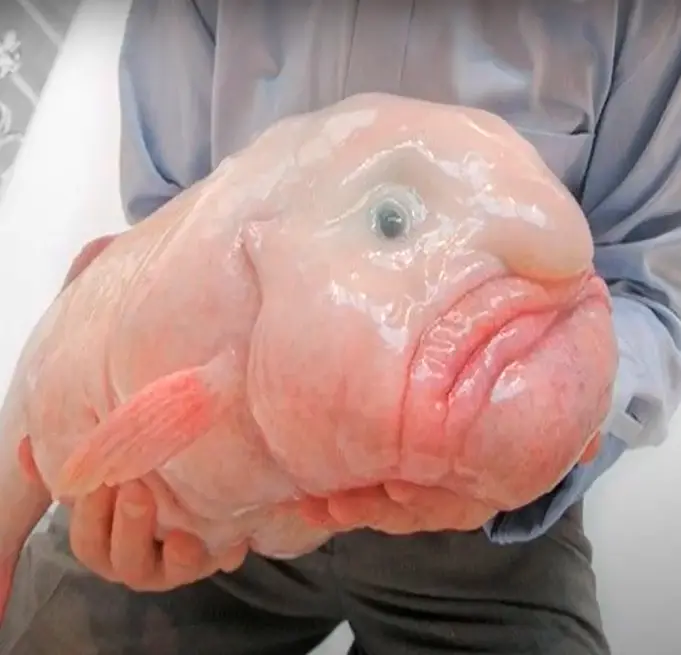
Blobfish do not have any real muscles. It is commonly found in the deep waters off mainland Australia, Tasmania, and New Zealand coasts and has a gelatinous and somewhat amorphous appearance.
This unique physical characteristic is due to the fact that their tissue is largely comprised of a watery, non-muscular substance rather than actual muscle fibers.
While it might seem surprising that an animal could function without any muscles, the blobfish has evolved a number of adaptations that enable it to survive despite its apparent lack of physical strength.
For example, the blobfish is able to regulate its buoyancy by varying the amount of oil in its body, and its cartilaginous skeleton helps to support its weight. Additionally, the blobfish’s slow-moving lifestyle and low metabolic rate mean that it does not require as much physical exertion as other types of fish might.
It is also worth noting that while blobfish do not traditionally have muscles, they possess some specialized tissues that perform similar functions. For instance, blobfish have a type of “muscular” tissue called smooth muscle, which is found in their gut and allows them to digest food.
Additionally, they have specialized cells called myofibrils, which are found in their skin and may help them make small movements or adjust their body shape to changing conditions.
How Do Blobfish Live Without Bones and Muscles?
As a gelatinous and sluggish creature, the blobfish has uniquely adapted to its environment. One striking adaptation is its lack of bones and instead has a cartilaginous backbone which provides minimal support. This allows the blobfish to survive in the deepest parts of the ocean, where the pressure is immense, and no bony creatures can survive.
The blobfish’s lack of muscles is compensated by its gelatinous body, which provides buoyancy, allowing them to float without wasting too much energy. This also makes them efficient predators, as they can easily snatch up prey that comes within their reach.
Also Read: Do Blobfish Lay Eggs? [Yes- Here is How]
Additionally, the blobfish has a highly reduced metabolism, allowing them to survive in harsh conditions with limited food resources. They consume small creatures that fall into their path, such as crabs and sea worms, and marine snow, the organic matter that floats down from the surface.
How Big Is a Blobfish?
Blobfish usually grow up to a foot in length. These unique pink-colored fish have a soft skeletal structure with relatively few muscles, allowing them to exist at great depths with limited energy expenditure.
Their bodies are also jelly-like in nature, which contributes to a slightly lower density than the water they live in. This property enables them to float gently above the sea floor, where they habitually dwell.
Apart from their distinct physical features, blobfish are known for their longevity. They can live for over 100 years, with some instances of records proving they can live beyond 130 years.
These low-energy creatures have very few natural predators and a slow rate of growth and reproduction, which helps them to survive in the harsh conditions of the deep ocean.
Does a Blobfish Have a Big Fluffy Nose?
A blobfish does not actually have a big fluffy nose. The swollen appearance of their facial features, including their noses, is a temporary physical change that occurs when they are brought up from the sea depths.
Blobfish are perfectly adapted to the high-pressure environment of the deep sea, and their bodies are designed to withstand that pressure. However, when they are brought up to the surface, the sudden change in pressure causes their bodies to expand rapidly. This can lead to their facial features, including their nose, appearing disproportionately large and bulbous.
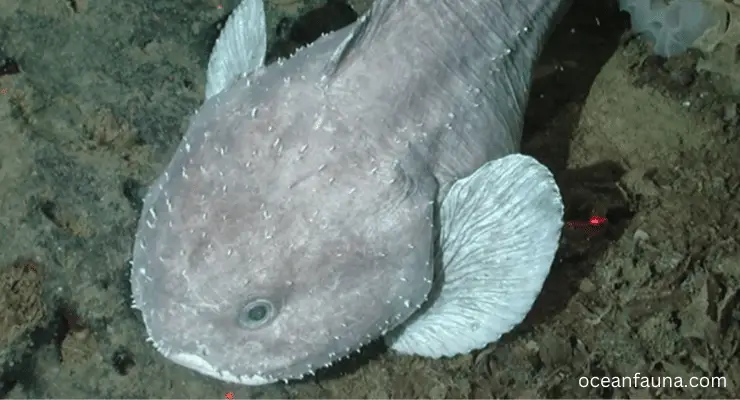

In their natural environment, blobfish actually have relatively small noses in proportion to the rest of their bodies. They are characterized by their gelatinous, blob-like bodies and droopy, frowning expressions, but their noses are not a defining feature.
Remember that, despite their unusual appearance, blobfish are a fascinating and important species in their own right. They are adapted to survive at depths where few other creatures can and play a vital role in their deep-sea ecosystem.
What Is the Digestive System of Blobfish?
The digestive system of blobfish begins in the mouth, where the fish typically ingests its food whole. Unlike humans and many other animals that use their teeth to chew food, the blobfish’s teeth are used solely for capturing prey. The swallowed food then travels down the esophagus and reaches the stomach.
The food is subjected to mechanical breakdown through churning in the stomach, facilitated by strong muscular contractions of the stomach walls. This is aided by the secretion of stomach acid and digestive enzymes, which help to further break down the food into smaller particles.
Also Read: Can You Eat Blobfish? [Is it Safe to Eat?]
From the stomach, the partially digested food passes into the small intestine, where most nutrient absorption occurs. The walls of the small intestine are lined with tiny projections called villi, which increase the surface area for absorption. The absorbed nutrients are then transported to the bloodstream and delivered to all the cells in the body.
The remaining waste products from digestion then travel to the large intestine, where water is absorbed and stool is formed. This waste is then eliminated through the rectum and anus.
Overall, the digestive system of the blobfish is designed to efficiently extract nutrients from whole prey while minimizing the need for chewing.
The stomach’s mechanism of churning and the secretion of digestive enzymes and stomach acid facilitate the breakdown of food particles for nutrient absorption in the small intestine. The waste elimination process is also crucial to maintaining the organism’s health.
Conclusion
Hopefully, you have understood that the blobfish is a boneless fish that also don’t have real muscles. But, instead of solid bones and muscles, they have a cartilaginous backbone and a gelatinous body that helps them survive at sea depths.
Despite their unusual appearance, they are perfectly adapted to live in these conditions and play an important role in their ecosystem.
If you want to know more about this fish, let me know. I will answer them as soon as possible.


3 thoughts on “Do Blobfish Have Bones? [Facts Explained]”