No, dolphins cannot smell since they have no olfactory nerves. But surprisingly, dolphins have an olfactory tract.
So, what is the purpose of their olfactory tract, then? Don’t worry. Everything will be discussed in this article.
Can Dolphins Smell?
The lack of olfactory nerves prevents any creature from detecting smells, including dolphins. Thus, dolphins cannot smell anything.
Olfactory nerves are responsible for transmitting sensations of smell from the nose to the brain. In humans, these nerves are located in the olfactory epithelium, a layer of tissue inside the nasal cavity that is highly sensitive and specialized to recognize odors.

Unfortunately, dolphins don’t have these olfactory nerves, so they are not able to detect or differentiate any kind of scent. Though some believe dolphins can smell through their blowholes, this simply isn’t true; blowholes only allow air into their lungs and do not function in any way like a nose does.
Furthermore, some species of marine mammals—especially whales—have also been known to produce distinctive scents for communication purposes, but even in these cases, dolphins cannot sense them due to their lack of olfactory organs.
This means that even if other creatures were releasing chemical signals into the water around them, dolphins would not be able to detect it with their noses or any other organ since they don’t have one that can do so effectively as humans do through theirs. For this reason, we must conclude that dolphins cannot smell anything at all and rely solely on their vision and hearing abilities when perceiving their environment.
What Is the Function of A Dolphin’s Olfactory Tract?
The function of a dolphin’s olfactory tract is believed to be related to the sense of taste as well as detecting chemical changes in the water. It appears that dolphins, although unable to smell, can detect chemicals dissolved in the water, providing them with information about their environment and potential prey.
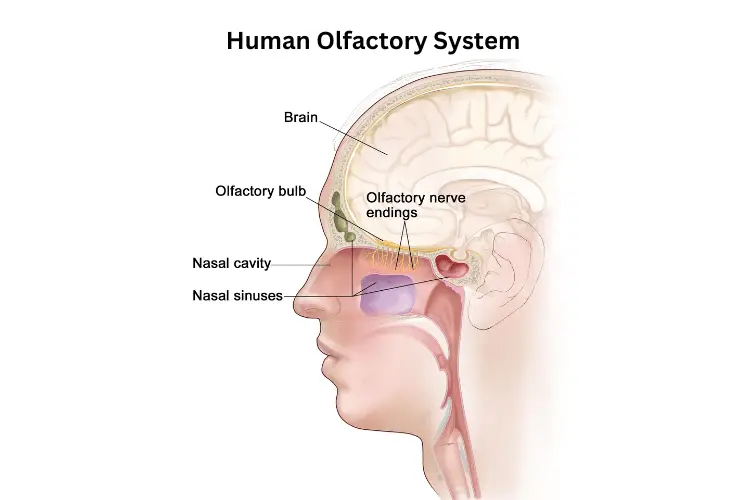
The olfactory tract is a tube connecting the nasal cavity to the back of the throat, which helps them discern different tastes and odors in their immediate area. Dolphins appear to use this structure to trace food sources, detect predators or other threats, or explore new areas with an increased capacity for analysis and information gathering.
Additionally, it has been suggested that dolphins’ olfactory tract can also detect hormonal cues from other dolphins as part of their social behavior, allowing them to recognize each other’s presence from a distance and even discriminate between family members.
This sense of taste and sensing chemical changes in their environment is believed to be especially useful for bottlenose dolphins which feed on fish near the ocean surface where chemical changes are more prominent.
How Do Dolphins Communicate?
Dolphins communicate using a combination of vocalizations, body language, touch, and chemical signals. Here is a more detailed explanation of how dolphins communicate:
Vocalizations:
Dolphins produce a wide range of vocalizations, including whistles, clicks, and pulsed calls. Whistles are used for a variety of purposes, such as attracting attention, maintaining group cohesion, and indicating individual identity. Clicks are used for echolocation, allowing dolphins to navigate, hunt, and identify objects in their environment. Pulsed calls are more complex vocalizations used for social interaction and communication.
Body language:
Dolphins also communicate using body language, including postures, gestures, and movements. For example, they may use tail slaps or body rolls to signal aggression or playfulness, and they may use head-butting or touching to demonstrate social bonding.
Touch:
Dolphins also communicate with each other by touching or rubbing against each other or by touching with their flippers. This kind of communication helps them keep social ties strong and gives comfort.
Chemical signals:
Dolphins release various types of chemical signals, such as hormones and pheromones. Pheromones are chemicals that can elicit a range of responses, such as attracting mates, marking territory, or signalling social status. Hormones, such as cortisol and testosterone, can act as chemical signals, regulating behavior and maintaining social order.
Do Dolphins Call Each Other By Name?
Yes, dolphins do call each other by name. Scientists believe that dolphins communicate and recognize each other through unique vocalizations or whistles, which are thought to act as individualized names. Research has found that dolphins produce signature whistles for their own use, which can be used to identify themselves to others in their pod.

They also seem to recognize the signature whistles of other dolphins even if they have never been in contact with them before. This suggests that they may use these unique vocalizations like a name in order to keep track of different individuals within their social group.
Additionally, it appears that dolphins can even remember the names of certain individuals over long periods of time – up to 20 years or more. This means that, much like humans, these aquatic creatures use their own special “names” to keep track of one another and establish important relationships within their pods.
Can Dolphins Taste?
Yes, dolphins can taste, though their sense of taste is not as developed as that of humans. Studies have found that while dolphins can still perceive salty flavors, they have lost the ability to identify any other tastes, such as sweet, sour, bitter, or umami. In some cases, it has been proposed that the loss of these flavors might be the result of evolution or adaptation in order to better suit their aquatic lifestyle and dietary requirements.
Dolphins rely heavily on their sense of hearing and sight to hunt for prey in their natural environment instead of relying on taste alone. However, research has also shown that dolphins still possess olfactory tracts connected with taste receptors in their mouths which enable them to detect changes in water chemistry when consuming food items. This suggests that although they may not be able to identify specific flavors as humans do, they can still experience certain tastes through a detection process.

Taste buds in dolphins are located mainly around the lips and tongue but have also been found along the walls of the oropharynx – the area at the back of a dolphin’s throat used for swallowing food – suggesting that they may also be able to perceive some flavor sensations while swallowing larger prey items.
Furthermore, studies have indicated that they may use gustatory hairs found in their blowholes and nostrils to identify potentially dangerous substances contained within prey before consuming them.
FAQs
How far can a dolphin smell?
Dolphins rely mostly on their other senses in order to communicate and live. They use sound and echolocation to find food, avoid predators, and recognize each other. Surprisingly, dolphins don’t have any olfactory (sense of smell) system.
While some species do have a rudimentary nose structure at the top of their heads, studies suggest that this is not well developed. This means that dolphins are basically “smell-blind.” No matter how far away something is, they won’t be able to tell what it is by its smell.
They will have to use their senses and rely on other physical properties like shape, size, color, sound, etc., to get a full picture of what they see. Dolphins likely have this problem because they live in water, where smells spread mostly through water and not through the air, and they didn’t need to be able to smell until they started hunting close up.
Can dolphins smell out of water?
Dolphins are interesting animals that have figured out a really cool way to live and grow in water. They can dive as deep as 300 meters to find food, but they can’t smell. Dolphins can’t smell anymore because they live in water. This is different from mammals that live on land. This means that they also can’t smell things above the water’s surface, so dolphins can’t smell out of the water.

Even though they can’t smell, dolphins have shown they are very smart and good at getting along with others using complex communication methods, like facial expressions and echolocation.
Can dolphins smell period blood?
No, dolphins can’t smell not only period blood but also any other.
Dolphins, the amazing sea-dwelling mammals known for their playful personalities and intelligence, rely more on other senses than smell. Instead of relying on their noses as land animals do, dolphins have acute hearing and eyesight to help them sense their environment.
Through a process called echolocation, they send out sound waves that bounce off objects in the water and form an image of the object in their brain. They then interpret this information to determine an object’s size, shape, and location relative to themselves.
Without a functioning sense of smell or an organ devoted to it, as found in terrestrial animals, dolphins remain oblivious if something is smelling “fishy” or not. So, unfortunately for curious minds everywhere, dolphins are unable to detect period blood–or anything else for that matter if only through smell.
Conclusion
So, it is clear that dolphins can’t smell because they don’t have the olfactory nerve. Although they have an olfactory tract, it doesn’t mean they use it for smelling. It has other usages discussed above. Now, if you have any questions regarding the matter, let us know.

