Sharks, one of the ocean’s ultimate predators, have an incredibly diverse appetite. They indulge in a feast of fishes, crustaceans, mollusks, marine mammals, and, yes, even their own kind. While some sharks are not too picky with their meals, certain species have developed a taste for specific delicacies.
Join me in this captivating blog as I unveil the fascinating world of what sharks devour and uncover the secrets of their feeding frenzy!
Which Factors Impact Shark Feeding?
Sharks are fascinating creatures. As apex predators, their feeding habits have always been of great interest. Several factors impact shark feeding. Here they are:
Water Temperature
Most sharks are cold-blooded animals, which means the surrounding environment regulates their body temperature. Water temperature plays a crucial role in shark feeding as it affects the digestion rate and metabolic rate of these creatures. Sharks tend to be less active in colder waters, and their feeding rate decreases.
Conversely, sharks are more active in warmer waters and have a higher feeding rate.
Tidal Pattern
Tidal patterns are also a key factor in shark feeding. Tides affect the movements of prey animals, which in turn impact the feeding behavior of sharks. During low tide, prey animals are often stranded in shallow water, making them an easy target for sharks.
On the other hand, prey animals tend to move farther away from the shore during high tide, making it harder for sharks to catch them.
Seasonal Changes
Seasonal changes also impact shark feeding patterns. During certain seasons, some shark species migrate to different locations in search of better feeding opportunities. Where in the summertime, the waters off the coast of California are usually filled with several types of sharks.
In winter, however, some shark species migrate to warmer waters in order to find food more easily. In addition, changes in water temperature and the availability of prey can also affect shark feeding behavior.
Size, Speed, and Strength of Prey
The size, speed, and strength of prey also play a significant role in shark feeding. Sharks typically prefer larger, slower-moving prey as they require less energy to catch.
However, some shark species, such as tuna and mackerel, are specifically adapted to hunt faster-moving prey. Sharks also prefer to feed on weaker and injured prey, making them an easier target.
Location and Availability of Prey
The location and availability of prey also impact shark feeding. Sharks tend to be found near areas where their preferred prey is abundant. For example, reef sharks are commonly found near coral reefs where there is a high density of fish.
Sharks are also opportunistic feeders and will eat whatever prey is available, even if it is not their preferred food source.
What Do Sharks Eat?

Sharks are known to be indiscriminate feeders, dining on various marine creatures that come their way. However, different shark species exhibit specific dietary preferences. Most sharks consume fish, squid, and crustaceans. Still, certain species have evolved to thrive on specific delicacies. Here are the details-
Do sharks eat marine mammals?
Sharks are recognized as formidable predators that have been observed consuming various prey items, including marine mammals. However, not all species of sharks have a diet that includes marine mammals. The dietary preferences of sharks can vary based on factors such as habitat and prey availability.
Although sharks have the ability to consume any prey that comes within their range, they primarily target marine mammals that are weaker, slower, and smaller in size. Consequently, sharks are less commonly prey upon certain marine mammals such as whales, dolphins, dugongs, manatees, and porpoises due to their larger size, greater speed, or inaccessibility.
Nevertheless, if sharks perceive these marine mammals to be weaker or smaller, they may still attempt to consume them.
Which marine mammals are common prey for sharks?
Several distinct species of sharks are recognized for their frequent predation on various marine mammals, including seals, sea lions, pinnipeds, and sea otters. Notably, the great white shark, tiger shark, and bull shark have gained notoriety for their predation on pinnipeds such as seals and sea lions.
These species of sharks have been observed attacking these marine mammals during their feeding migration towards their mating or birthing locations by ambushing them from below and taking them by surprise.
Additionally, several factors play a role in determining which marine mammals a shark will target, including the location, the availability of other prey items, and the seasonality.
For example, some species of sharks, such as the white shark, prefer to consume elephant seals when they are molting, as these seals are slow and have limited mobility during that time.
Do sharks eat fish?
Yes, sharks are known for consuming different types of bony and cartilaginous fish. Sharks have a varied diet, and their choice of prey may depend on their species, location, and size. Bony fishes are part of the diet of many shark species, and they may consume different types of fish ranging from sardines and anchovies to tuna and mackerel.
Sharks have a specialized jaw that allows them to bite and tear through the flesh of their prey. Unlike most bony fishes, sharks possess several rows of sharp, serrated teeth that they use for ripping and shredding their prey into smaller pieces that are easier to swallow.
Do sharks eat crustaceans?
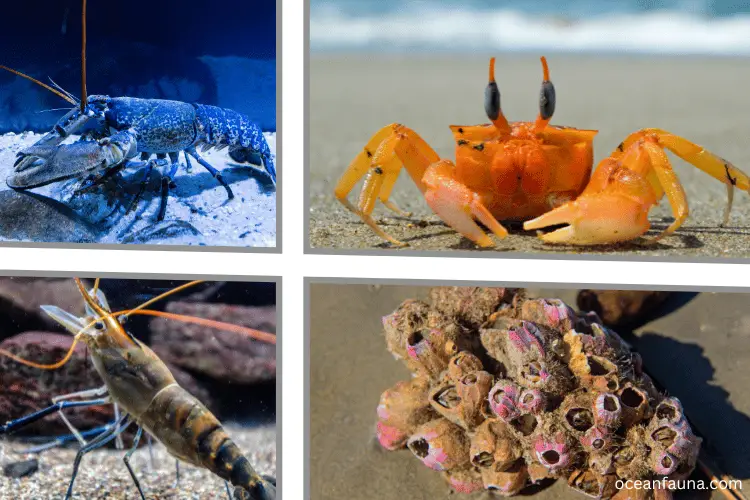

Sharks eat crustaceans like lobsters, crabs, shrimp, and barnacles. These marine animals are important in the ocean food chain, providing nutrition for sharks and other predators. Different shark species consume various crustaceans based on size and habitat.
For example, larger sharks like great whites and tiger sharks eat larger species such as lobsters and crabs. Smaller sharks like pygmy sharks and lantern sharks prefer smaller crustaceans like shrimp and krill. Even baby sharks also consume these crustaceans.
Lobster: Lobsters are among the most popular crustaceans that sharks feed on. They are typically found in rocky areas of the ocean floor and are known for their hard exoskeletons that protect them from predators. However, sharks have powerful jaws and sharp teeth that enable them to break through the shells and consume the tender meat inside.
Crab: Crabs are another favourite food source for sharks, especially the blue crab, which is a delicacy in many parts of the world.
Shrimp: Shrimp is also a common food source for sharks, particularly smaller species that cannot consume larger prey.
Do sharks eat octopus?
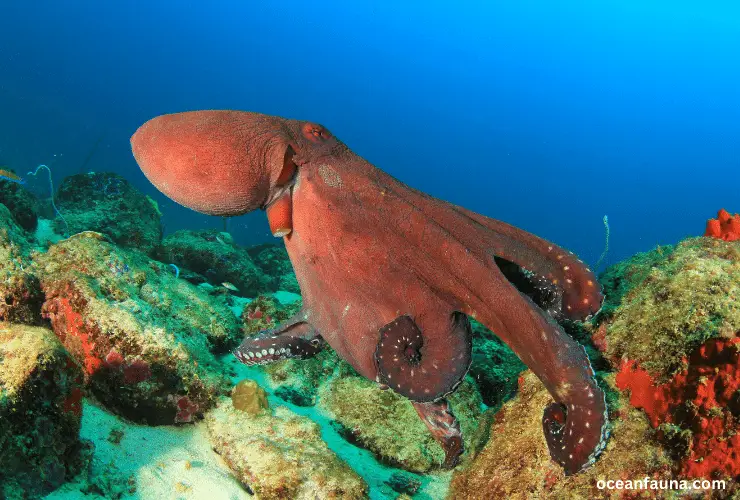

Yes, sharks do eat octopus, and it is not uncommon for a variety of shark species to consume these cephalopods. Some of the most common species of sharks that feed on octopuses include bull, hammerhead, great white, and blue sharks.
Octopuses are known to inhabit a variety of marine environments, including rocky shores, coral reefs, and the deep sea. Despite their ability to camouflage and evade predators, they cannot always escape the jaws of a hungry shark.
In fact, sharks are among the most efficient apex predators in the ocean, and they have developed a range of hunting strategies that enable them to capture even the most elusive prey.
Do sharks eat Mollusks?
Yes, sharks do indeed eat mollusks, with octopuses and squid being particularly common prey. Mollusks consist of a diverse group of invertebrate animals that include not only cephalopods such as octopuses and squid but also gastropods (snails and slugs), bivalves (clams, oysters, and mussels), and others.
Sharks are known to have a varied diet that includes both vertebrates and invertebrates. While some species of sharks prefer to feed on fish, others have been observed to actively seek out and consume mollusks.
Both octopuses and squid are considered high-quality food sources for sharks as they provide a good balance of nutrients and are relatively easy to catch due to their slower mobility compared to fish.
Do sharks eat penguins?

Yes, sharks eat penguins when food is scarce. Great whites, hammerheads, and tiger sharks target these birds for sustenance. However, sharks don’t solely rely on penguins as their main food source. They only resort to feeding on them when there are no other options.
Great whites, especially, have an advantage over penguins due to their speed and agility. Their sharp teeth and powerful jaws can easily catch and consume fast-moving birds. Hammerhead and tiger sharks also prey on penguins in certain locations but are not as common predators as great whites.
Do sharks eat sea turtles?
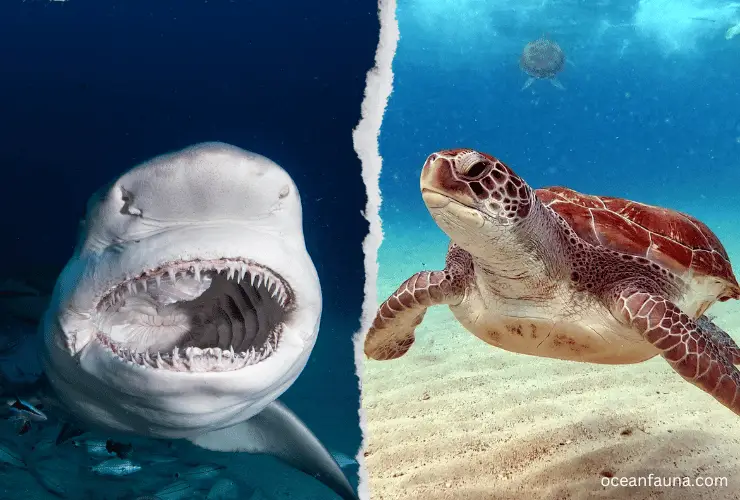

Yes, sharks eat sea turtles, one of their favourite food sources. Great White sharks and Tiger sharks are known for preying on sea turtles. With their sharp teeth, they can easily tear apart their prey.
Hammerhead sharks also feed on sea turtles, using their wide head shape to pin them down against the ocean floor. Hammerhead sharks often hunt juvenile sea turtles that are still developing their swimming abilities.
Do sharks eat jellyfish?
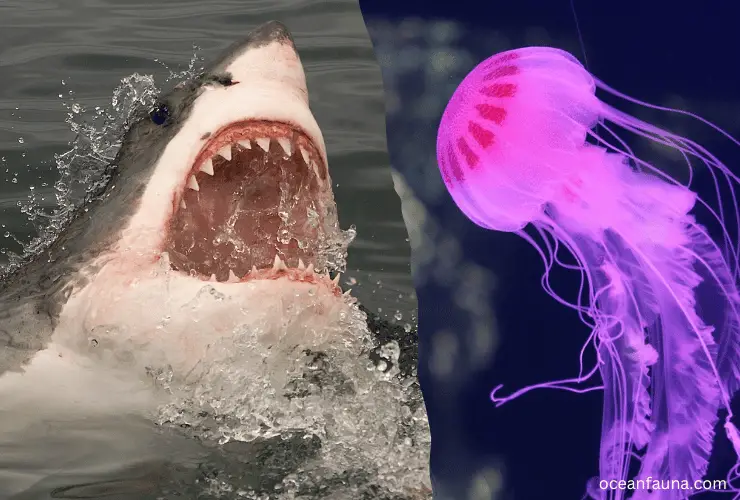
Yes, sharks do eat jellyfish, but it is not their primary food source. As opportunistic predators, sharks will feed on various prey, depending on what is available. Jellyfish are often found in the same areas where sharks feed, so they do encounter them.
However, not all species of sharks eat jellyfish. For example, the great white shark primarily feeds on fish and does not typically eat jellyfish. On the other hand, some species of sharks, such as the large and slow-moving whale sharks, will consume a large amount of jellyfish along with plankton.
While sharks can and do eat jellyfish, they can also be vulnerable to the stings of certain species of jellyfish. For example, the box jellyfish is known to be one of the most venomous creatures in the world and can kill a shark.
Do sharks eat stingrays?
Yes, some sharks do eat stingrays, and among those sharks, hammerhead sharks are particularly known for their taste for stingrays. This is because stingrays are one of the major food sources for hammerhead sharks, and they have adapted to specialize in hunting and consuming this prey.
While hammerhead sharks are the most well-known examples of stingray-eating sharks, other shark species have also been observed eating stingrays. For instance, tiger sharks (Galeocerdo cuvier) are also known to prey on stingrays, as are blacktip sharks (Carcharhinus limbatus), bull sharks (Carcharhinus leucas), and nurse sharks (Ginglymostoma cirratum).
In general, sharks that inhabit the same coastal waters as stingrays are more likely to consume them, as they are readily available and easy to catch.
Do sharks eat seabirds?
Yes, Sharks eat seabirds. They have a varied diet, including seabirds and other prey. Great white sharks, found worldwide in coastal and offshore waters, prey on birds like gulls and albatrosses. In one study off the coast of South Africa, researchers observed the sharks killing at least 34 Cape Gannets over two years.
Sharks may also consume already dead or injured seabirds. For example, a study of bull sharks in a Florida estuary found they had eaten various prey, including drowned or deceased seabirds.
Do sharks eat other sharks?

Yes, Sharks do eat other sharks. Cannibalism is common among sharks as they are omnivores and opportunistic feeders. Some species, like the great white shark, attack and consume their own kind. This is often seen in juvenile or smaller sharks still developing and lacking hunting skills to catch other prey.
Sharks also engage in intra-specific competition, competing for resources like food, mating opportunities, and territory. Larger sharks are dominant predators in their habitats and prey on smaller sharks. For example, bull and tiger sharks attack and eat smaller species like blacktip sharks.
Not all shark species practice cannibalism or intra-specific competition. Filter feeders like the whale and basking sharks only consume small planktonic organisms. Hence, feeding habits vary greatly across shark species.
Do sharks eat humans?
Despite popular belief and the media’s depiction of sharks as human killers, sharks do not typically eat humans. As mentioned in the background context, humans are not a part of their natural diets, and sharks typically prefer to feed on fish and marine mammals.
In fact, according to the International Shark Attack File, there were only 66 confirmed unprovoked shark attacks on humans worldwide in 2020, and only 10 of those were fatal. While any shark attack is tragic and should be taken seriously, the chances of a shark actually attacking and consuming a human are incredibly low.
Furthermore, not all shark species have been known to attack humans. Of the over 500 species of sharks, only about a dozen have been involved in attacks on humans. These species include the Great White Shark, Tiger Shark, and Bull Shark, which are known to be more aggressive and potentially dangerous to humans.
It’s also worth pointing out that most shark attacks on humans are cases of mistaken identity. Sharks may mistake humans for prey, such as seals or fish, due to their similar shape and movement in the water. Once a shark realizes that a human is not their intended prey, they will typically release them and move on.
What Do Baby Sharks Eat?
Baby sharks, also called shark pups, primarily eat small prey like crustaceans (lobsters, crabs, shrimps) and cephalopods (squids). Consuming this smaller prey provides vital nutrients and energy for their growth and development.
When young, baby sharks find it challenging to hunt larger prey due to their size and inexperience. As a result, they rely on small prey to sustain themselves.
Interestingly, some species of baby sharks practice intrauterine cannibalism by consuming their siblings while still in the egg. This behavior, seen in species like the sand tiger shark, helps the largest embryo gain more resources and increase its chances of survival.
Can Sharks Be Herbivores?
Are sharks herbivores? Well, sharks, you see, are not complete herbivores. They’re not just meat-eaters either. Actually, most sharks are carnivores, but did you know that some species actually munch on plants and algae? Yep, it’s true! These sharks, known as omnivorous, have quite a diverse diet.
They chow down on a mix of meat and plants. They’ll go after smaller fish, squid, and crustaceans, but they’re not picky! They’ll also happily munch on seaweed and kelp, especially if there’s a meat shortage in their neck of the woods. Pretty interesting, huh?
Not all sharks are created equal when it comes to their diet. For instance, the largest shark in the world, the whale shark, is not a meat-eater at all. Instead, it feeds mainly on plankton and small fish, using its massive mouth to filter out the tiny creatures from the water.
Similarly, the basking shark, the second-largest species after the whale shark, mostly feeds on small, planktonic animals.
How Do Sharks Catch Their Prey?

Sharks are known to be fearsome hunters, and their predatory abilities are largely attributed to their highly efficient sensory receptors known as lateral lines. These lateral lines enable the sharks to detect any movement or changes in pressure in the water, which alerts them to the presence of potential prey.
This system transforms pressure changes in the water into electrical impulses that the shark’s brain interprets as sound, allowing them to sense the slightest disturbance in the water around them.
Once the shark detects the presence of prey, it uses its excellent eyesight and sense of smell to locate its target. Sharks’ eyes have adapted to work well in low light conditions and can detect even the slightest movement, while their sense of smell is incredibly sensitive, allowing them to detect blood and other odors from miles away.
When it has located its prey, the shark will swoop in, often at high speed, using its powerful body to generate a burst of acceleration that propels it toward its target. Sharks rely on their sharp teeth to capture prey, which they use to rip off chunks of flesh and feed on nutrient-rich tissues.
However, they cannot chew their food effectively, so they need time to properly digest what they have consumed.
Sharks typically consume between 0.5% and 3% of their body weight per meal and usually space their meals out over several days. This is because their digestive systems are not designed to cope with large amounts of food at once and require time to break down the nutrients to absorb them properly.
When Do Sharks Eat?
Sharks are efficient predators with diverse feeding habits. Some feed during daylight, while others are active at night. For example, the great white shark stalks and surprises prey during the day, while the tiger shark identifies prey using its excellent sense of smell at night.
Sharks can be opportunistic feeders or have specific feeding times. The blue shark feeds in the early morning and late afternoon, while the whale shark prefers night feeding.
Some sharks migrate to different areas seasonally for feeding, driven by prey availability, water temperature, and ocean currents. The great hammerhead shark migrates to warmer waters during winter, while the tiger shark migrates to the cool, nutrient-rich waters of the southern hemisphere in summer to feed on seals, dolphins, and other marine mammals.
Do sharks eat all day?
No, sharks do not eat all day. They have a slow metabolism due to being cold-blooded. Unlike humans, who eat multiple times a day to maintain energy levels, sharks can survive without food for extended periods.
Sharks also have a unique digestive system that can’t handle large amounts of food at once. They typically consume only a small percentage (0.5% – 3%) of their body weight per meal and spread it out over several days. This allows their digestive system to properly break down and absorb nutrients.
For example, a great white shark weighing around 1,500 pounds might eat up to 45 pounds of food per meal but could go several days or even a week between meals. Some species, like the frilled shark, have been observed going without food for up to six months.
Additionally, some shark species have adapted to survive without food for even longer periods. The sand tiger shark, for instance, can go months without eating by storing large amounts of fat and oil in its liver as an energy source.
While sharks don’t commonly eat all day, certain species, like the great white shark, have been observed feeding for several hours straight when they encounter a large source of food, such as a school of fish or a whale carcass.
Conclusion
Hopefully, you have detailed information regarding shark predation. If you have doubts about sharks’ diet, you can ask me.
No matter which species you are considering, sharks have evolved to be adept predators and can consume a wide range of prey items, including stingrays and sea birds. Knowing this can help us understand these apex predators’ role in their ecosystems and how they interact with other species.


1 thought on “What Do Sharks Eat? [All about Sharks’ Diet]”